Corporate Laptop to local lab
Make local lab accessible from corporate Laptop
Let’s imagine a scenario where you are operating from your home, equipped with enhanced user privileges on a computer running Windows. Your corporate machine is filled with snake oil, and you are prohibited from installing software such as Docker. For the sake of this scenario, let’s also assume that Cisco AnyConnect supervises your routing and promptly restores it if you attempt to manually modify it. Your personal lab, situated right next to you, remains idle. It’s a resource you can utilize to boost your productivity for fun and profit.
Find a route with some space(IP-Adresses) on your Interface(192.168.0.188):
REM to much routes for manual inspection
route print | find /c /v ""
2303
REM Find at least one /24 network
route print *.*.*.0 | findstr 192.168.0.188
Netzwerkziel Netzwerkmaske Gateway Schnittstelle Metrik
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.188 25
52.112.0.0 255.252.0.0 192.168.0.1 192.168.0.188 25
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 Auf Verbindung 192.168.0.188 281
[filtered to protect the innocent and the guilty]
224.0.0.0 240.0.0.0 Auf Verbindung 192.168.0.188 281
192.168.0.0 looks promissing(own network):
route print 192.168.0.0
Aktive Routen:
Netzwerkziel Netzwerkmaske Gateway Schnittstelle Metrik
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 Auf Verbindung 192.168.0.188 281
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 Auf Verbindung 192.168.0.190 291
192.168.0.0 255.255.255.0 10.180.128.1 10.180.141.4 2
I can’t change the metric despite my user rights(Cisco AnyConnect).
Let’s “steal” some IPs from 52.112.0.0 (AS8075 Microsoft Corporation)
What could possibly go wrong :-)
Install a new ipv4 static route on your router (/28): Example:
|Netzwerk |Subnetzmaske |Gateway |
|---------- |------------- |---------- |
|52.112.0.0 |255.255.255.240 |192.168.0.1 |
52.112.0.1 - 52.112.0.14 are useable internally now
I use DHCP on my network. For Windows we can use a static second IP for a “DHCP interface” add with the following commands:
netsh interface ipv4 show interface
REM Let's assume "Ethernet 3" is what we want.
netsh interface ipv4 set interface interface="Ethernet 3" dhcpstaticipcoexistence=enabled
netsh interface ipv4 add address "Ethernet 3" 52.112.0.3 255.255.255.240
netsh interface ipv4 show addresses
Konfiguration der Schnittstelle "Ethernet 3"
DHCP aktiviert: Ja
IP-Adresse: 52.112.0.3
Subnetzpräfix: 52.112.0.0/24 (Maske 255.255.255.0)
IP-Adresse: 192.168.0.181
Subnetzpräfix: 192.168.0.0/24 (Maske 255.255.255.0)
Standardgateway: 192.168.0.1
...
netsh interface ipv4 show interfaces "Ethernet 3"
Parameter für die Schnittstelle "Ethernet 3"
-------------------------------------------------------------
...
Koexistenz von DHCP/statischer IP : enabled
'''
Windows: Allow remote desktop (RDP) connections.
Install openssh daemon to have a smooth experience with tunnels and so on. openssh for windows. To enable remote tunnels and connect from any client:
C:\ProgramData\ssh\sshd_config
...
AllowAgentForwarding yes
AllowTcpForwarding yes
GatewayPorts yes
...
mstsc.exe:
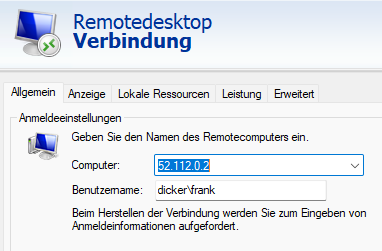
For convenience, you can extend the hosts file with host entries for which you have opened a remote tunnel
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts:
...
52.112.0.3 jira.devops.T.de
...
Alternative: If your router supports it, you can utilize port forwarding to your devices and make use of the tunneling features provided by ‘putty’.