self-signed certificate
TLS certificate verification process during hHandshake
-
Client Hello: The client sends a message to the server listing the supported encryption and hash algorithms, as well as the supported protocol versions.
-
Server Hello: The server responds with a message indicating the selected encryption and hash algorithms, along with the protocol version it wishes to use. This message also contains the server’s certificate.
-
Client Certificate Verification: The client verifies the certificate received from the server for validity. This process involves several steps:
- Certificate Validity: The client checks if the certificate is currently valid.
- Signature Verification: The client verifies the signature of the certificate using the public key of the Certificate Authority (CA) that signed the server’s certificate. If the signature is valid, the client can be assured that the certificate is not forged.
- CA’s Public Key: SSL/TLS certificates are signed by a Certificate Authority (CA). The CA uses its private key to digitally sign the certificate, and the corresponding public key of the CA is included in the certificate itself.
- Signature Extraction: The client first extracts the signature from the server’s certificate received. The signature is included in the certificate along with other metadata such as the server’s public key.
- Hash Value Calculation: The client extracts the hash value of the certificate content. This hash value is then used to verify the validity of the signature. The hash value is calculated over the unsigned parts of the certificate, usually over the ASN.1 encoded bytes. This includes fields such as the certificate version, serial number, signature algorithm, validity period, public key, and issuer information. The calculation is typically performed using a cryptographic hash algorithm such as SHA-256.
- Signature Decryption: The client decrypts the signature using the CA’s public key contained in the CA’s certificate.
- Hash Value Comparison: After decrypting the signature, the client compares the calculated hash value of the certificate content with the hash value obtained by decrypting the signature. If the two hash values match, the signature is considered valid.
- Trust in the Certificate Authority: In addition to signature verification, the client verifies whether it trusts the Certificate Authority (CA) that issued the certificate. This is done by the client extracting and using the CA’s public key from its own pre-installed certificates.
- Certificate Chain: The client also verifies if the certificate is part of a trusted certificate chain by checking if it knows and trusts the public key of the issuing CA. This step is important to ensure that the server certificate was issued by a trusted source.
-
Key Exchange: After successful certificate verification, the client proceeds with the key exchange to establish a secure channel for communication with the server.
-
Handshake Completion: Upon completion of the handshake, the client and server are ready to exchange encrypted data
X.509 certificate description.
Below are some bash scripts that create the certificates and the JKS container.
Create self-signed certificates
make_certs.sh
#!/bin/bash
RED_FG="\033[31m"
NORM="\033[0m"
BLINK="\033[5m"
BLUE_BG="\033[44m"
GREEN_BG="\033[42m"
check_return_code() {
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo
echo -e "$RED_FG$BLINK=============================================================================$NORM"
echo -e "$RED_FG$BLINK $NORM$RED_BG$BOLD $0: $* $NORM"
echo -e "$RED_FG$BLINK=============================================================================$NORM"
echo
exit 1
fi
}
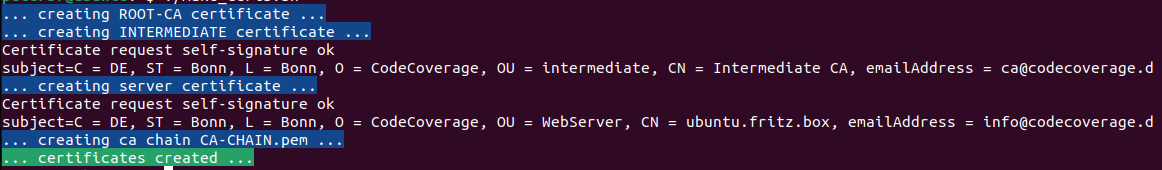
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating ROOT-CA certificate ...$NORM"
mkdir -p ~/certs
# read -p "Press any key to continue... " -n1 -s
cd ~/certs || { echo -e "$BOLD$RED_FG... certs directory not found ...$NORM" && exit; }
# ROOT CA key with passphrase
openssl genrsa -aes256 -passout pass:'CAPASS' -out CA.key 4096
# ROOT Cert one year
openssl req -x509 -new -key CA.key -sha512 -days 365 -out CA.pem -passin pass:'CAPASS' \
-subj '/C=DE/ST=Bonn/L=Bonn/O=CodeCoverage/OU=Root/CN=Root CA/emailAddress=ca@codecoverage.d'
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating INTERMEDIATE certificate ...$NORM"
## Intermidiate certificate
# key
openssl genrsa -aes256 -passout pass:'INTER' -out INTER.key 4096
# create request
openssl req -new -sha512 -out inter.csr -key INTER.key -passin pass:'INTER' \
-subj '/C=DE/ST=Bonn/L=Bonn/O=CodeCoverage/OU=intermediate/CN=Intermediate CA/emailAddress=ca@codecoverage.d' \
-addext 'basicConstraints = critical,CA:true'
check_return_code "$(($LINENO-1)) openssl Intermediate cert failed"
# sign intermediate
openssl x509 -req -in inter.csr -CA CA.pem -CAkey CA.key -passin pass:'CAPASS' -CAcreateserial -out INTER.pem \
-days 730 -sha512 -copy_extensions=copyall
check_return_code "$(($LINENO-1)) openssl signing Intermidiate cert failed"
## Generating Intermediate-Authenticated Certificates
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating server certificate ...$NORM"
# Generating CLIENT KEY
openssl genrsa -aes256 -passout pass:'CERT_KEY' -out ubuntu.fritz.box.key 2048
# Generating certificate request
openssl req -new -key ubuntu.fritz.box.key -sha512 -out ubuntu.fritz.box.csr -passin pass:'CERT_KEY' \
-subj '/C=DE/ST=Bonn/L=Bonn/O=CodeCoverage/OU=WebServer/CN=ubuntu.fritz.box/emailAddress=info@codecoverage.d' \
-addext 'subjectAltName = DNS:*.fritz.box,DNS:ubuntu.fritz.box,IP:127.0.0.1' \
-addext 'keyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment'
# sign server certificate to use with itermediate cert
openssl x509 -req -in ubuntu.fritz.box.csr -CA INTER.pem -CAkey INTER.key -passin pass:'INTER' \
-CAcreateserial -out ubuntu.fritz.box.crt -days 730 -sha512 -copy_extensions=copyall
check_return_code "$(($LINENO-1)) openssl version to old ?"
# print client key
#openssl rsa -noout -text -in ubuntu.fritz.box.key -passin pass:'CERT_KEY'
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating ca chain CA-CHAIN.pem ...$NORM"
cat CA.pem INTER.pem > CA-CHAIN.pem
# print client cert
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... printing intermediate cert ...$NORM"
openssl x509 -noout -text -in INTER.pem
# print server cert
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... printing server cert ...$NORM"
openssl x509 -noout -text -in ubuntu.fritz.box.crt
echo -e "$BOLD$GREEN_BG... certificates created ...$NORM"
TLS1.2 Round-Trips
The full TLS 1.2 handshake requires 2 round-trips + 1 for TCP/IP
Client Server
| |
| ---- ClientHello -----------------------> |
| |
| <--- ServerHello, Certificate, ---------- |
| ServerKeyExchange, ServerHelloDone |
| |
| |
| ---- ClientKeyExchange, ChangeCipherSpec, |
| Finished --> |
| |
| <--- ChangeCipherSpec, Finished --------- |
openssl x509 -startdate -enddate -in ubuntu.fritz.box.crt -noout
will print the validity of the certificate
openssl verify -CAfile CA-CHAIN.pem ubuntu.fritz.box.crt
to check the cain.
Create Java Keystore
make_jks.sh
#!/bin/bash
NORM="\033[0m"
BLINK="\033[5m"
BOLD="\033[1m"
BLUE_BG="\033[44m"
BLUE_FG="\033[34m"
RED_FG="\033[31m"
RED_BG="\033[41m"
GREEN_BG="\033[42m"
BLUE_FG="\033[34m"
BLUE_BG="\033[44m"
check_return_code() {
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo
echo -e "$RED_FG$BLINK=============================================================================$NORM"
echo -e "$RED_FG$BLINK $NORM$RED_BG$BOLD $0: $* $NORM"
echo -e "$RED_FG$BLINK=============================================================================$NORM"
echo
exit 1
fi
}
getIssuer()
{
openssl x509 -noout -text -in "${1}" -certopt no_header,no_version,no_serial,no_signame,no_validity,no_subject,no_pubkey,no_sigdump,no_aux,no_extensions 2>/dev/null | sed 's/^[^:]*://g'
check_return_code "getIssuer() failed!"
}
getSubject()
{
openssl x509 -noout -text -in "${1}" -certopt no_header,no_version,no_serial,no_signame,no_validity,no_pubkey,no_sigdump,no_aux,no_extensions,no_issuer 2>/dev/null | sed 's/^[^:]*://g'
check_return_code "getSubhect() failed!"
}
certificate=~/certs/ubuntu.fritz.box.crt
keyfile=~/certs/ubuntu.fritz.box.key
ca_dir=~/certs
password=CERT_KEY
passwordQuery="pass:"$password
alias=~/certs/ALIAS
openssl rsa -check -noout -passin $passwordQuery -in "$keyfile"
check_return_code "opening ssl-key \"$keyfile\" failed"
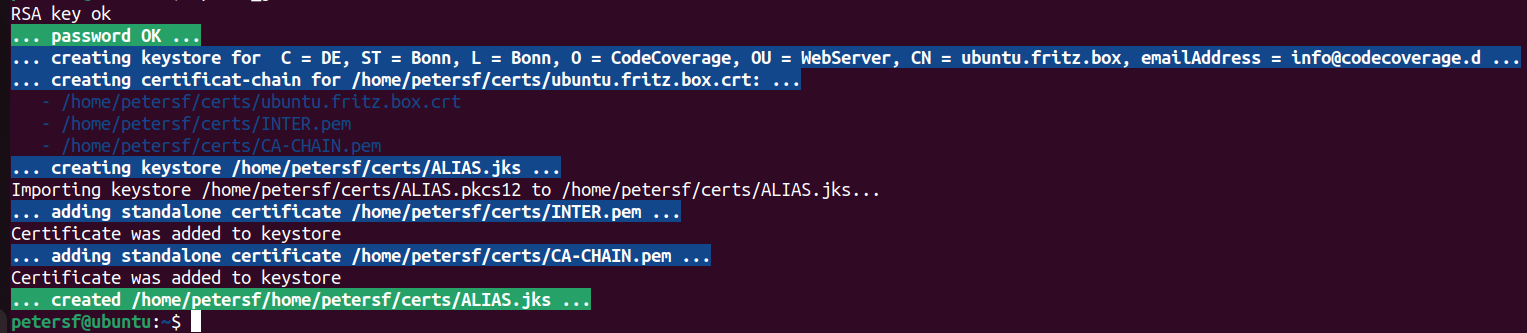
echo -e "$BOLD$GREEN_BG... password OK ...$NORM"
issuer=$(getIssuer $certificate)
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating keystore for $(getSubject $certificate) ...$NORM"
while [ -z "`echo $result|fgrep \"$issuer\"`" ];
do
result="$result $issuer"
for ca_pem in $ca_dir/*.pem;
do
subject=$(getSubject "$ca_pem");
if [ "$issuer" = "$subject" ];
then
issuer=$(getIssuer "$ca_pem")
ca_certs="$ca_certs $ca_pem"
break
fi
done
done
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating certificat-chain for $certificate: ...$NORM"
for f in $certificate $ca_certs;
do
echo -e "$BLUE_FG - $f$NORM"
done
rm .makejks.cer $alias.jks
for f in $certificate $ca_certs; do cat "$f" >> .makejks.cer; echo >> .makejks.cer; done
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... creating keystore $alias.jks ...$NORM"
openssl pkcs12 -inkey "$keyfile" -in .makejks.cer -export -passin pass:$password -passout pass:$password -out $alias.pkcs12 -name $alias
keytool -importkeystore -keypass $password -srcstorepass $password -srckeystore $alias.pkcs12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -deststoretype pkcs12 -deststorepass $password -destkeystore $alias.jks -destalias $alias -srcalias $alias
for cert in $ca_certs;
do
aliasname=${cert##*/}
aliasname=${aliasname%.*}
echo -e "$BOLD$BLUE_BG... adding standalone certificate $cert ...$NORM"
keytool -importcert -file "$cert" -keystore $alias.jks -alias "$aliasname" -noprompt -storepass $password
done
rm -f $alias.pkcs12
echo -e "$BOLD$GREEN_BG... created $(pwd)$alias.jks ...$NORM"
Java test program
Simple java test driver
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.security.KeyStore;
import javax.net.ssl.KeyManagerFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLServerSocket;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket;
public class TLSServer {
private static final String CONTENT =
"<html>" +
"<head><title>Simple SSL Server</title></head>" +
"<body><h1>--...---</h1></body>" +
"</html>";
private static void sendStaticHttpResponseAndReadInput(SSLSocket sslSocket) throws IOException {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(sslSocket.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(sslSocket.getOutputStream()));
String inputLine;
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
if (inputLine.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
}
out.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n");
out.write("Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
out.write("Input-Empty: " + inputLine.isEmpty() + "\r\n");
out.write("Content-Length: " + CONTENT.length() + "\r\n");
out.write("\r\n");
out.write(CONTENT);
out.flush();
in.close();
out.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
char[] pwd = "CERT_KEY".toCharArray();
KeyStore keystore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
keystore.load(new FileInputStream("/home/petersf/certs/ALIAS.jks"), pwd);
KeyManagerFactory kmf = KeyManagerFactory.getInstance(KeyManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm());
kmf.init(keystore, pwd);
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
sslContext.init(kmf.getKeyManagers(), null, null);
SSLServerSocketFactory sslServerSocketFactory = sslContext.getServerSocketFactory();
SSLServerSocket sslServerSocket = (SSLServerSocket) sslServerSocketFactory.createServerSocket(8443);
while (true) {
try {
SSLSocket sslSocket = (SSLSocket) sslServerSocket.accept();
sslSocket.startHandshake();
System.out.println(sslSocket.getLocalSocketAddress());
System.out.println(sslSocket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
sendStaticHttpResponseAndReadInput(sslSocket);
sslSocket.close();
} catch (Throwable t ) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}
}
}
Some commands to check the functionality
openssl s_client -showcerts -servername server -connect 127.0.0.1:8443
curl --cacert ~/certs/CA-CHAIN.pem -tlsv1.2 -vvv https://127.0.0.1:8443